
Images were merged to identify overlapping signals (merge, yellow). After fixation, cells were stained for (C) acetylated tubulin (ac-tubulin) or (D) γ-tubulin to visualize the axoneme or the basal body of the primary cilium, respectively. Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding GFP–RMND5A for 24 h and then further serum-starved (high glucose DMEM, 0.5% FCS) for an additional 24 h to induce ciliogenesis.
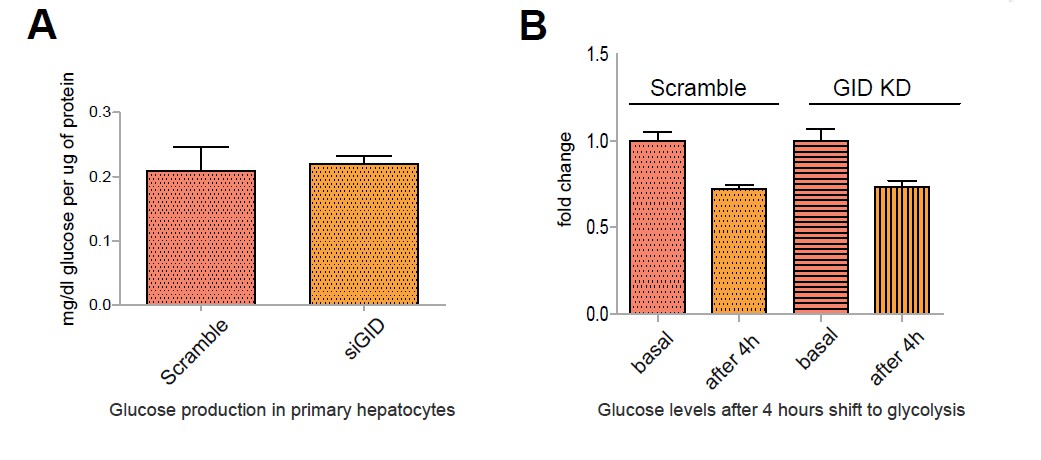
(C,D) RMND5A localizes to the basal body of the primary cilium in NIH-3T3 cells. A large number of transporters, structural proteins, membrane receptors and basal body-located factors function in the primary cilium. (B) Schematic model of the primary cilium, composed of a basal body, axoneme and ciliary membrane. (A) Schematic model of the vertebrate GID complex and its known subunits RING domain-containing subunits are highlighted in blue, the substrate-recruiting factor GID4 is highlighted in red. GID subunits colocalize to the basal body of mono-ciliated cells. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd. laevis results in ciliopathy-like phenotypes, we suggest that GID subunits are candidate genes for human ciliopathies that coincide with defects in SHH signal transduction.ĪMPK Ciliopathies Cilium GID complex Sonic hedgehog Ubiquitin. Since our data reveal a critical function of the GID complex at the primary cilium, and because suppression of GID function in X. Despite correct localization of SHH signaling components at the primary cilium and functional GLI3 processing, we find a prominent reduction of some SHH signaling components in the cilium and a significant decrease in SHH target gene expression. Furthermore, we report SHH signaling pathway defects that are independent of AMPK and mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) activation.
We show that GID complex subunits localize to cilia in both Xenopus laevis and NIH3T3 cells. Here, we reveal that the GID complex is an integral part of the cilium required for primary cilia-dependent signal transduction and the maintenance of ciliary protein homeostasis. Our recent studies have shown that loss of GID ubiquitin ligase function results in aberrant AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and elongated primary cilia, which suggests a functional connection to cilia. Cilia are evolutionarily conserved organelles that orchestrate a variety of signal transduction pathways, such as sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling, during embryonic development.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
